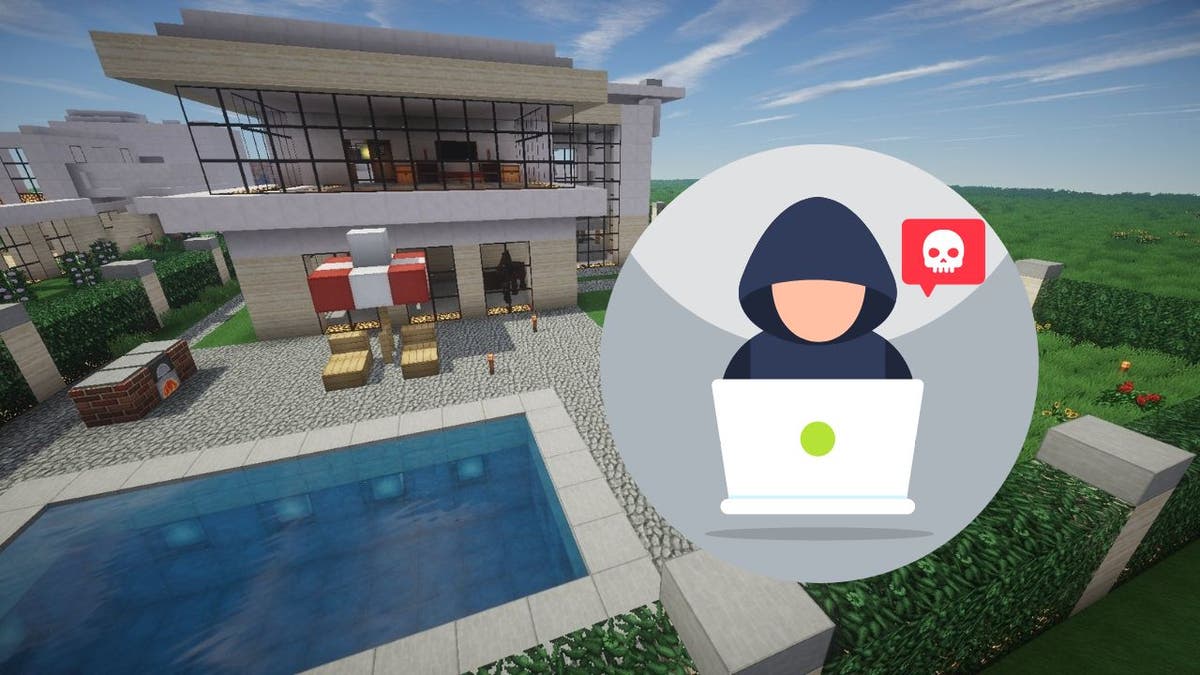
The popular video game Minecraft, with its massive community of over 140 million active players, has become the target of a real-world threat: infostealing malware. Unlike the game's typical virtual adversaries, this danger poses a significant risk to players' personal data and online security.
Cybercriminals have infiltrated the Minecraft modding community through compromised developer accounts on platforms like CurseForge and Bukkit. These platforms, known for sharing and creating game modifications (mods), have been exploited to distribute infected modpacks. When players download these seemingly harmless packs, the malware stealthily installs itself on their devices.
This large-scale cyberattack has affected millions of downloads and can have serious consequences. The malware can steal sensitive information, including cryptocurrency transactions, Discord authentication tokens, and even saved login credentials from browsers. It primarily targets Linux and Windows systems, with a significant number of victims in the United States.
The malware's tactics have evolved since its initial detection in April 2023, becoming increasingly sophisticated. It specifically targets Minecraft modders and developers, often exploiting the Windows Sandbox environment used for testing. The malware attempts to compromise the clipboard, aiming to infiltrate the host system.
This incident underscores the importance of robust cybersecurity practices, especially for online gamers. Downloading mods and plugins exclusively from trusted sources is crucial. Maintaining up-to-date antivirus software on all devices is also essential for protection against malware and other online threats.
This attack serves as a stark reminder that online threats extend beyond the virtual world of the game. Gamers must remain vigilant and proactive in protecting their digital security to fully enjoy the creative and immersive experience that Minecraft offers.
For a detailed list of affected plugins and further information, please refer to the resources provided by cybersecurity researchers.