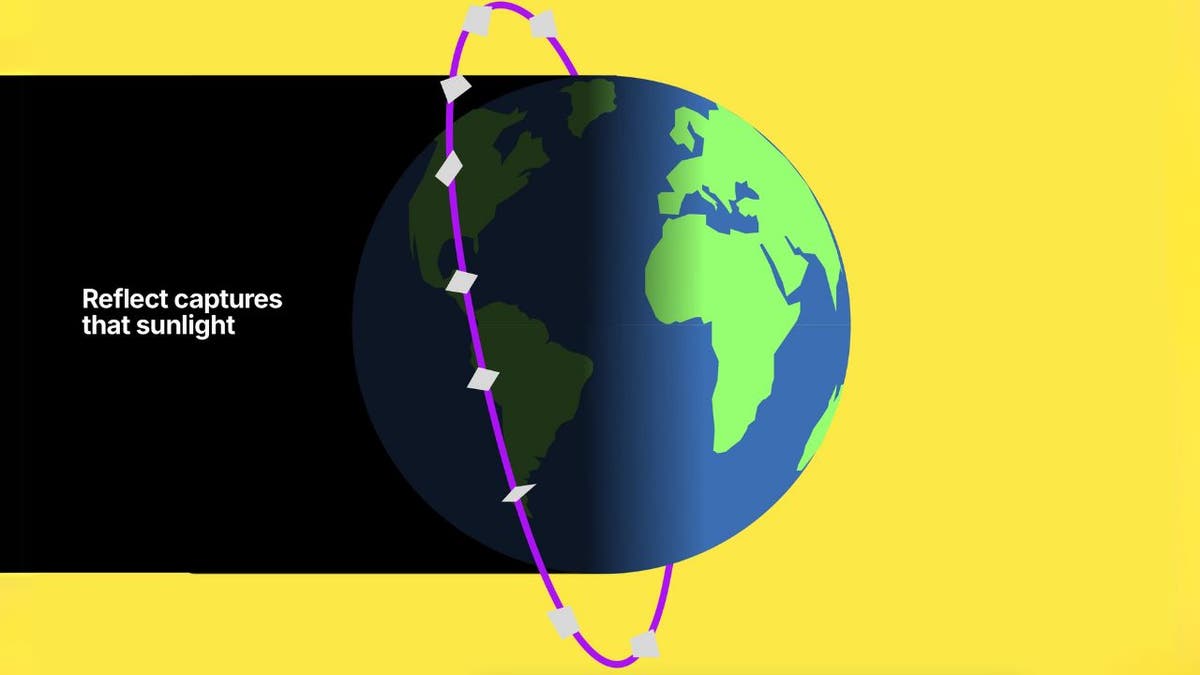
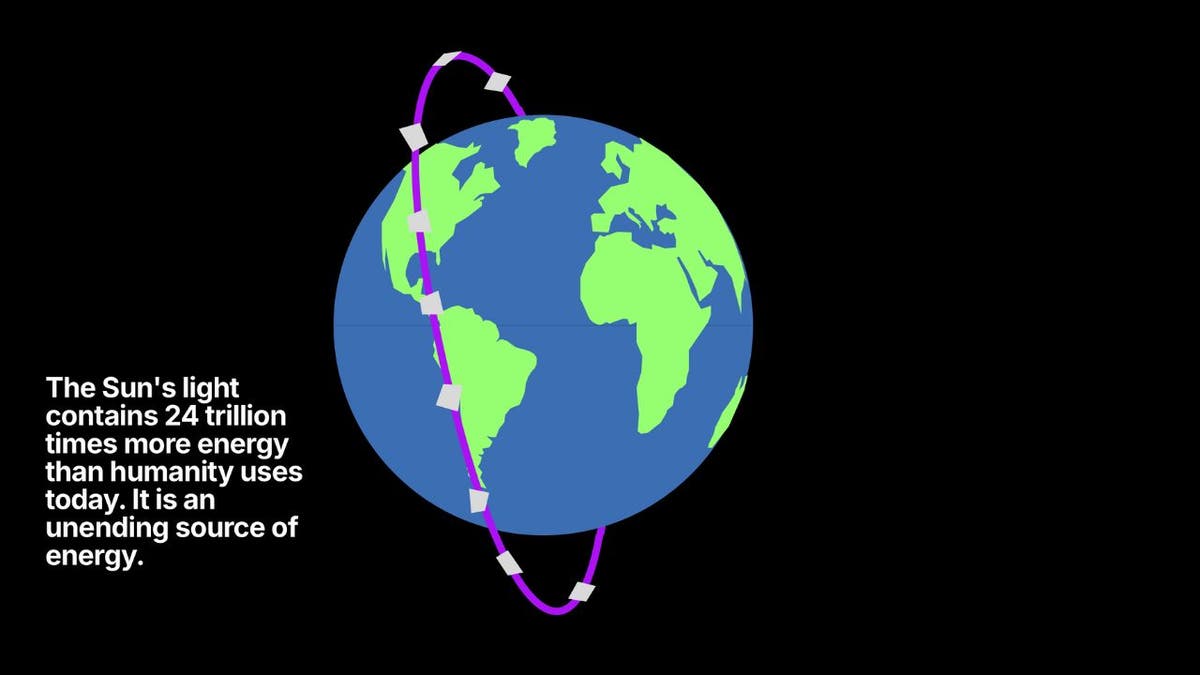
In a groundbreaking development for renewable energy, Reflect Orbital, a startup founded by Tristan Semmelhack and Ben Nowack, is working on a system to harness the sun's power even at night. Their ambitious project involves a network of mirrors in space, designed to reflect sunlight down to Earth, effectively offering daylight on demand. This innovative approach taps into the sun's immense energy potential – a staggering 24 trillion times greater than our current global energy consumption.
How This Space-Based Solar Reflection Works
Reflect Orbital plans to position satellites approximately 370 miles above Earth. These satellites will be equipped with 33-square-foot Mylar mirrors, highly reflective to maximize sunlight capture. The reflected light will illuminate a 3-mile-wide area on Earth for roughly four minutes per pass. This technology could revolutionize solar farm operations by extending their energy production beyond daylight hours.
Potential Applications and Impact
The potential impact of space-based solar reflection is vast, spanning several sectors:
- Enhanced Solar Farm Productivity: Providing sunlight to solar farms at night could significantly boost their output.
- Sustainable Urban Lighting: Cities could potentially utilize reflected sunlight for street lighting, reducing energy costs and environmental impact.
- Disaster Relief: In disaster zones lacking power, this technology could offer vital illumination for rescue and recovery efforts.
- Continuous Industrial Operations: Industries like construction, often limited by daylight hours, could operate around the clock.
Users, including individuals, businesses, and governments, would request light by submitting GPS coordinates online.

Overcoming Technical Hurdles
Reflect Orbital faces considerable technical challenges, such as atmospheric scattering, cloud cover, and the precision required to direct sunlight from orbit. To tackle these issues, they've enlisted experts from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory to validate the project's scientific foundation and feasibility.
Investment and Future Roadmap
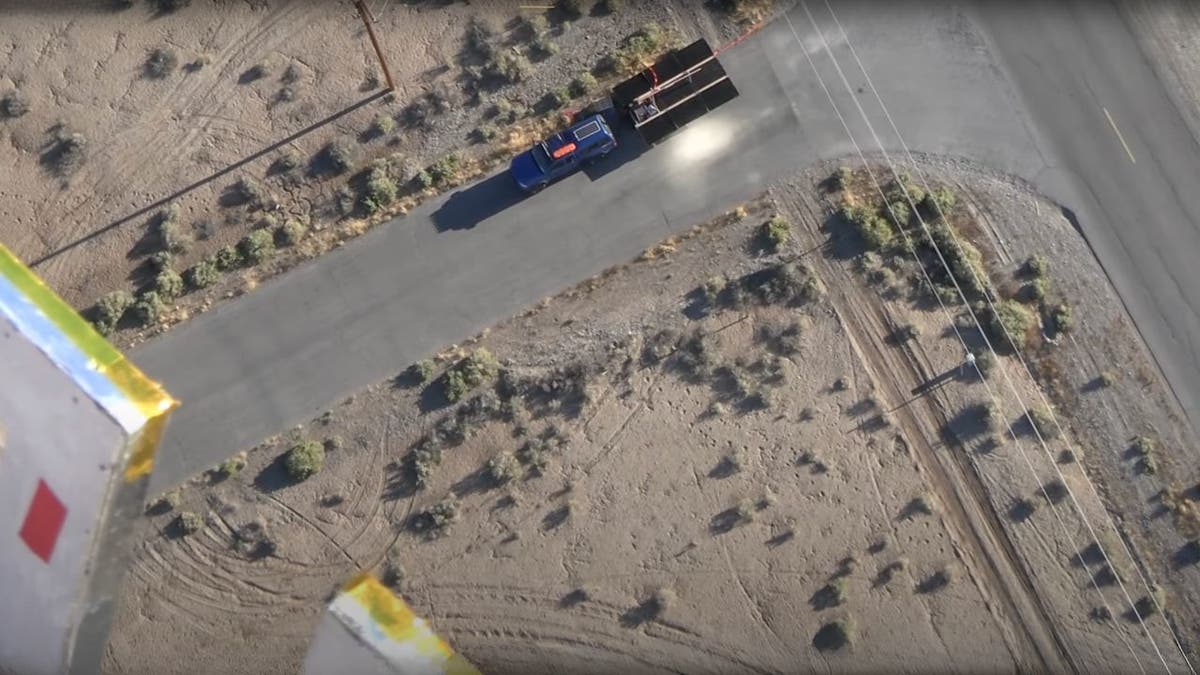
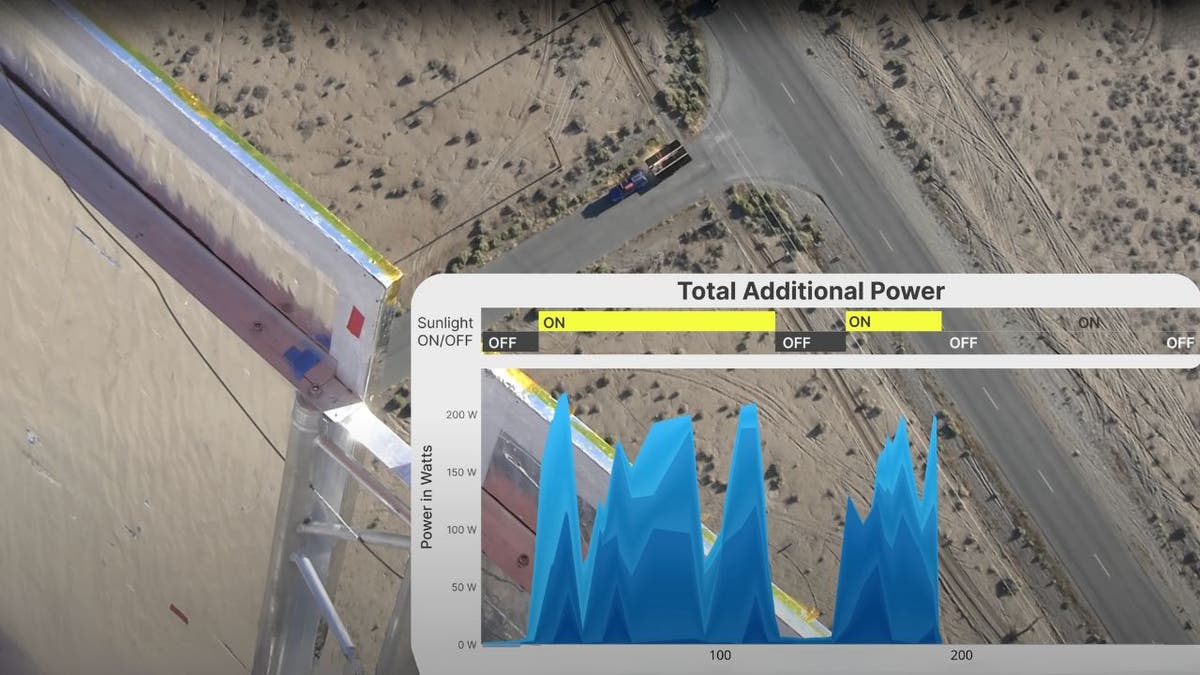
Reflect Orbital recently secured $6.5 million in seed funding, led by Sequoia Capital – their first space investment since SpaceX in 2020. The company has conducted successful tests using a hot-air balloon and a large mirror and aims to launch its first space-based sunlight service by the end of 2025. Their current objective involves a constellation of 57 satellites in sun-synchronous orbit to provide an extra 30 minutes of sunlight to solar farms worldwide.

Looking Ahead
While ambitious, Reflect Orbital's concept is based on established scientific principles and has attracted substantial investment. This innovation could be pivotal in addressing global energy challenges and promoting a sustainable future. As the project progresses, the world awaits the potential dawn of a new era in solar energy utilization.