Experiencing frequent crashes on your Windows computer? Whether it's persistent freezing, unexpected shutdowns, or a barrage of error messages, a malfunctioning PC can be incredibly disruptive. Fortunately, several straightforward solutions can help restore your system's stability. This guide presents nine practical fixes you can implement at home to address these crashing issues.

A man working on a PC (Kurt "CyberGuy" Knutsson)
1. Verify Cable Connections
Begin by confirming that all cables are securely connected to your computer. This often-overlooked step can resolve many crashing problems. For desktops, double-check connections at the back of the PC and consider testing a different power outlet to eliminate potential electrical issues. If you're comfortable with it, open the desktop case and ensure all internal PCI connections and power supply cables are firmly in place.

Wires coming out of a desktop PC tower (Kurt "CyberGuy" Knutsson)
2. Address Overheating
Overheating is a frequent culprit behind system crashes. Excessive heat can cause the CPU or graphics card to shut down to prevent damage. Signs of overheating include excessive heat emanating from the computer, a hot laptop casing, or unusually loud fan noise. To combat overheating, clean the internal fans using compressed air, ensuring adequate airflow around the computer. Avoid placing desktops under desks, as this can restrict airflow and contribute to dust accumulation.

A man working on a PC (Kurt "CyberGuy" Knutsson)
3. Utilize Safe Mode
If cable connections and overheating aren't the issue, try booting your PC into safe mode. This mode runs Windows with minimal drivers and files, helping identify software or hardware conflicts. While in safe mode, you can analyze Windows error logs and perform diagnostics. The process for entering safe mode differs slightly between Windows 10 and 11 (detailed instructions for both are provided in the original article).
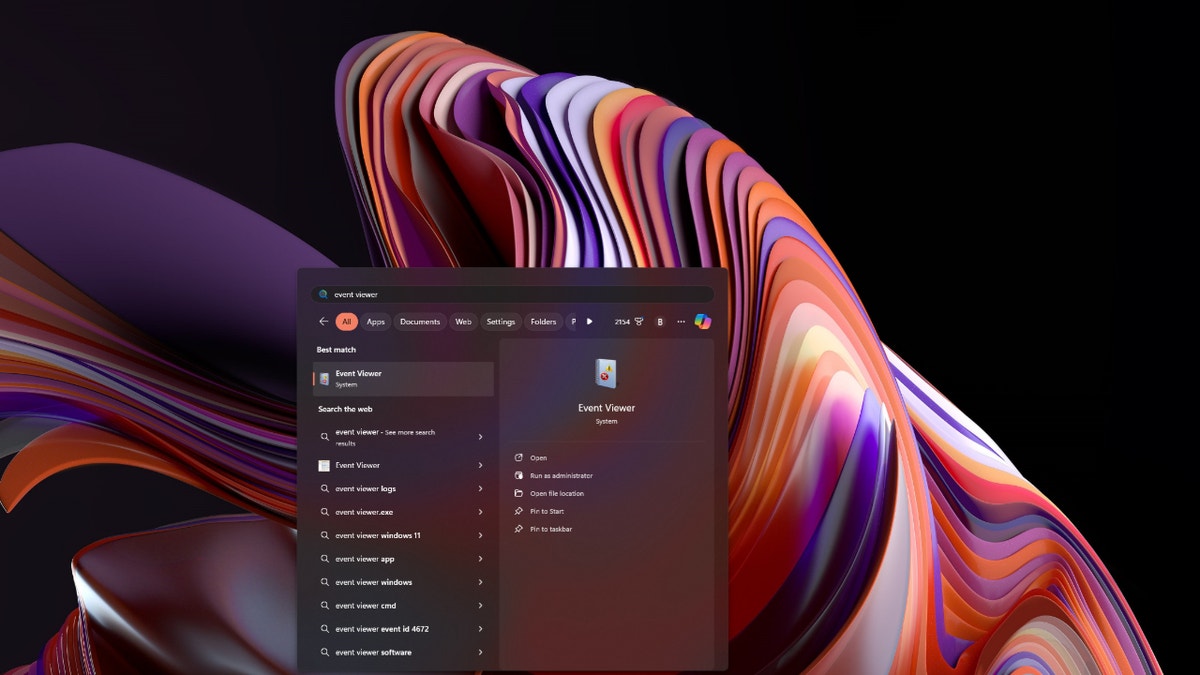
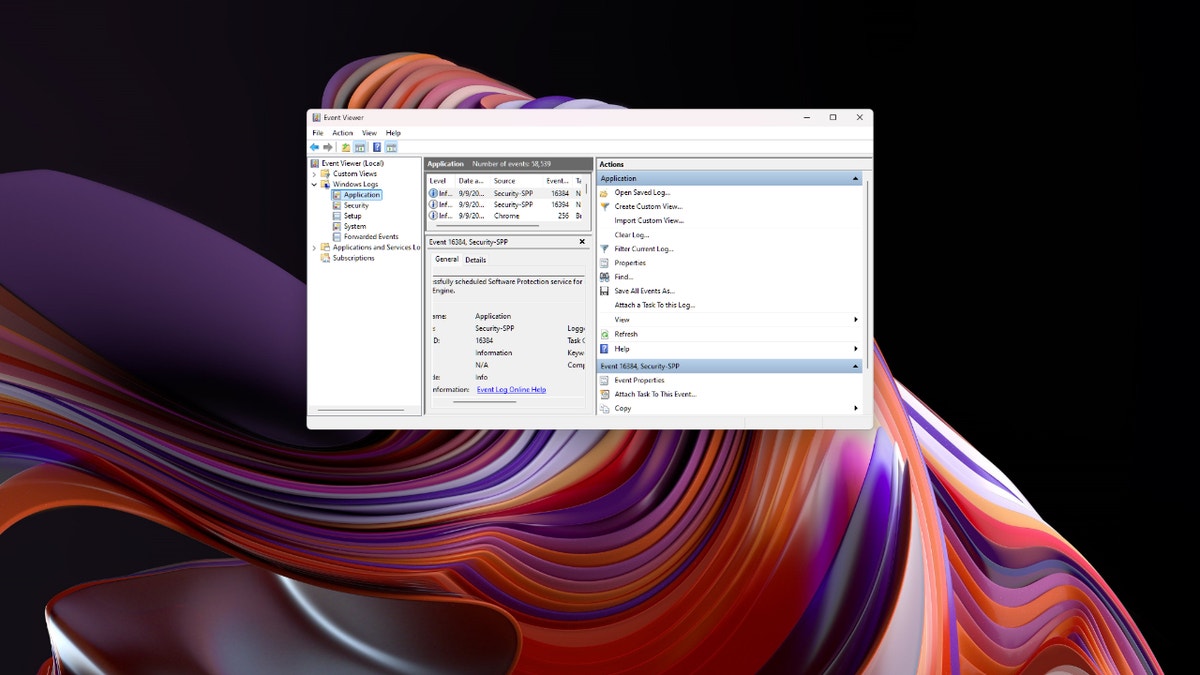
4. Examine Windows Error Logs
Access the Event Viewer to analyze Windows error logs. Search for "Event Viewer" in the Start menu, open the app, and navigate to Windows Logs (Application or System). Review the error codes associated with the crashes, then research these codes online for potential solutions.
Steps to boot into safe mode (Windows 11) (Kurt "CyberGuy" Knutsson)
Steps to boot into safe mode (Windows 11) (Kurt "CyberGuy" Knutsson)
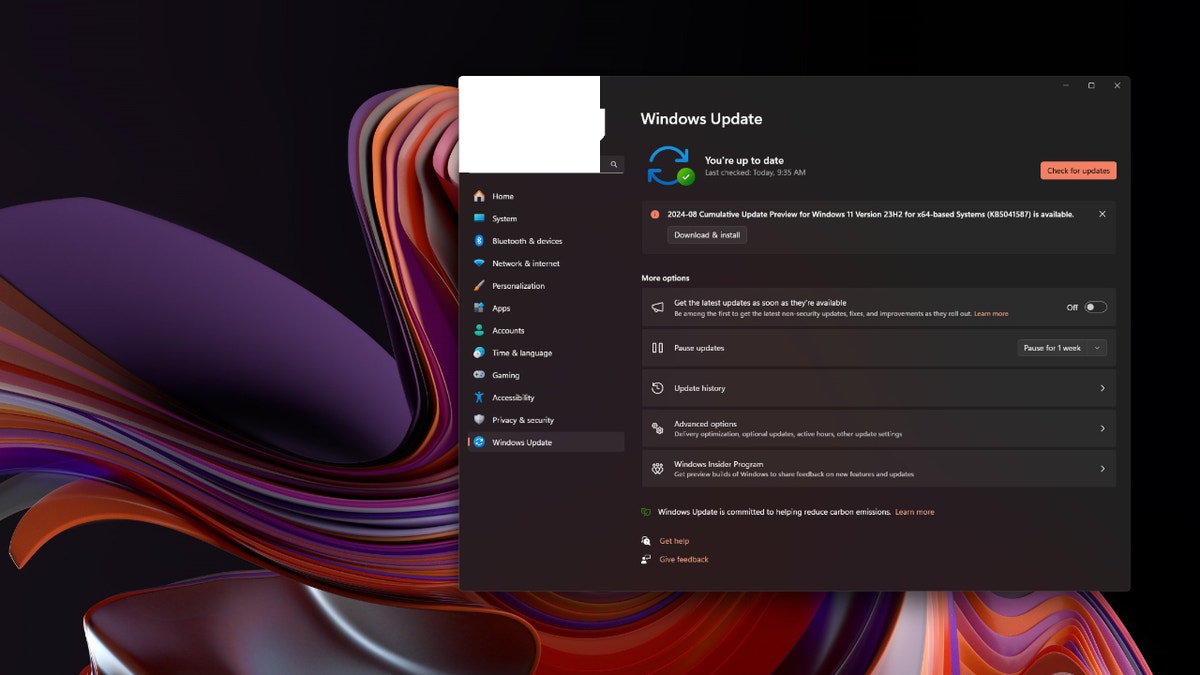
5. Update Your Operating System
An outdated Windows version can cause conflicts and crashes. Ensure your system is up-to-date by navigating to Settings > Windows Update and checking for available updates.
Steps to perform an OS update Steps to perform an OS update (Kurt "CyberGuy" Knutsson)
6. Conduct an Antivirus Scan
Run a scan using Windows Defender or your preferred antivirus software. This can identify and eliminate malware that might be contributing to system instability. (Instructions for using Windows Defender are provided in the original article.)
7. Check Hard Drive for Errors
Use the Command Prompt (run as administrator) to check your hard drive for errors. Type "sfc /scannow" and press Enter. This process scans for and attempts to repair corrupted files. If errors persist, you may need to replace your hard drive and reinstall Windows.
8. Diagnose RAM Issues
Problems with RAM can also trigger crashes. Use the Windows Memory Diagnostics tool (accessible by pressing Windows Key + R, typing "mdsched.exe," and pressing Enter) to check for RAM issues. A restart and memory check will be performed. If problems are detected, RAM replacement might be necessary.
9. Perform a System Restore
As a last resort, consider a system restore to revert your OS to a previous state before the crashes started. This can resolve software-related issues but will result in the loss of recent files and settings. (Instructions for performing a system restore are provided in the original article.)








